How Segmentation and Personalization Enhance Satisfaction, Engagement, & Conversions



“The customer is always right”, right?
“The customer is always right”, right?
Well, whether or not you agree with that old axiom, perhaps you can agree on this; in today’s world customer expectations are at a peak. More than ever before, customers expect personalized experiences that cater to their specific needs, and businesses that fail to meet these expectations risk losing both engagement and conversions. Today, everyone is special. Everyone demands therefore to be treated as such. If not, they'll go somewhere else. In some twisted way, the consumer controls capitalism more than they understand. For CRM managers, customer experience teams, and marketing professionals, the challenge is clear: How can you leverage customer data to deliver tailored, impactful experiences that drive results and keep them coming back for more? The answer relies on two essential strategies: segmentation and personalization.
In this article, we will explore how effective segmentation and personalization can lead to higher customer satisfaction, better engagement, and ultimately improved conversion rates. Sounds like a tall order, but, we’re sure that by the end of this article you’ll have gained some actionable insights into implementing key strategies that a proven to drive successful business outcomes. Of course, every business is unique and different, so WHICH strategies you apply and HOW you apply them is where the real magic lies.
What is Segmentation and Personalization?
The terms “personalization” and “segmentation” might already have some meaning to us. However, in todays context, segmentation and personalization refer to your understanding of your customers and how you tailor your interactions / messages accordingly. Let’s break these terms down further;
- Segmentation is the practice of dividing a customer base into distinct groups based on shared characteristics. This can be based on factors such as demographics, behaviour, psychographics, or geography. For example, sales teams will often divide their efforts into “territories” such as EMEA, or APAC.
- Personalization takes this one step further by using the insights gained from segmentation to craft individualized messages and offers that resonate with each specific customer or segment. So, using the example of EMEA, we further break down this territory into categories such as marketing people, sales people and IT / tech people.
Finding the balance in personalization; While hyper-personalization can enhance customer experience, it requires significant resources. It's essential to find the right balance that suits your business needs.
Here’s a table that gives an overview of the pros and cons of segmentation and personalization
Here’s a table that gives an overview of the pros and cons of segmentation and personalization
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized Customer Messages | Higher relevance and engagement with customers | Time-consuming to tailor messages for multiple segments |
| Customer Experience | Improved customer satisfaction and loyalty | Requires detailed customer data analysis |
| Targeted Campaigns | More effective targeting leads to higher conversion rates | Increased complexity in campaign management |
| Resource Allocation | Allows for better allocation of marketing budget | May require more tools, software, or staff to manage |
| Data Utilization | Maximizes the value from customer data | Risk of overwhelming data collection and analysis |
| Market Segmentation | Better segmentation leads to clear understanding of needs | More updating / maintaining segments is necessary (although AI can help) |
| ROI Potential | Higher potential return on investment (ROI) | Initial setup costs for tools, staff training, or consultants |
| Brand Loyalty | Builds stronger relationships with specific segments | Risk of alienating non-targeted groups if too niche |
| Scalability | Scalable strategies for growth and retention | Not easily scalable without increasing workload proportionately |
Why is segmentation important for personalization?
Segmentation is the first step toward building a more customer-centric approach. By identifying the unique needs and preferences of different groups within your customer base, you can deliver more targeted, meaningful messaging. The term “stereotype” might spring to mind -and yes, while many of us hate the idea of stereotypes and stereotyping people in general, the truth is that stereotypes are helpful for us to break down large groups of people into smaller groups. So, in the world of marketing and sales, we can say that stereotypes help us to “divide and conquer”.
In the next section we will cover some typical types of segmentation you can expect to come across. Some of these might be familiar to your, while others might be new.
Common segmentation groups
1. Demographic Segmentation:
- Definition: Segments customers based on quantifiable traits like age, gender, income, education, and occupation.
- Use: Helps companies tailor products and marketing messages to the general characteristics of specific population segments. For instance, you might want to target younger consumers with trendy, fashionable products, and higher-income individuals with luxury goods such as expensive watches.
2. Behavioural Segmentation:
- Definition: Segments your customers based on their behaviour toward a brand, such as purchase frequency, brand loyalty, product usage, and benefits sought.
- Use: Helps businesses identify and target specific customer actions, like offering rewards to loyal customers or promotions to first-time buyers. For instance, you might notice that some customers in your data tend to order from a few select brands only. Armed with this knowledge, you could, for example, offer loyalty discounts to these customers.
3. Psychographic Segmentation:
- Definition: Segments your customers based on psychological attributes, such as lifestyle, personality, values, and social status.
- Use: Enables brands to connect with customers on a deeper emotional level by aligning products and messages with their interests, beliefs, and values. While psychographic segmentation is a bit harder to crack, the idea is to
4. Geographic Segmentation:
- Definition: Segments customers based on their physical location, such as country, city, climate, or population density.
- Use: Allows businesses to adjust their marketing and product strategies according to regional preferences, cultural differences, or climate needs.
5. Technographic Segmentation:
- Definition: Divides customers based on their technology usage and preferences, including devices, software, and platforms they use. You know those Windows people that always complain about how Apple MacBook’s are overpriced and lack performance? That’s a technographic segment of your audience!
- Use: Helps companies in tech-related industries customize offerings based on customer familiarity and interaction with certain technologies, such as mobile apps or social media platforms.
6. Firmographic Segmentation:
- Definition: Applies to B2B markets and groups businesses based on organizational attributes like company size, industry, revenue, and location.
- Use: Enables B2B marketers to tailor strategies based on company characteristics, such as targeting large enterprises with complex solutions or small businesses with cost-effective options.
7. Needs-Based Segmentation:
- Definition: Groups customers based on their specific needs, preferences, or problems they aim to solve with a product or service.
- Use: Allows brands to address distinct customer needs with customized solutions, ensuring that products meet the specific demands of different customer groups.
8. Value-Based Segmentation:
- Definition: Segments customers based on the value they bring to the company, usually in terms of profitability or lifetime value.
- Use: Helps businesses allocate resources efficiently by focusing on high-value customers who contribute the most to the company's revenue, providing premium services or exclusive offers to retain them.
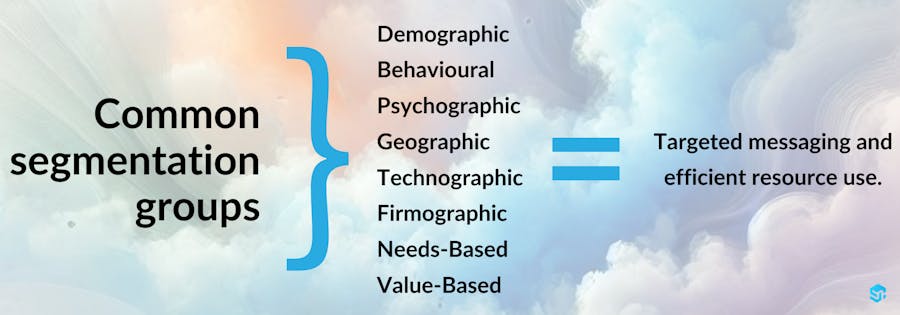
By understanding these segments, marketing teams (and sales teams) can better craft their messaging so that it is more relevant and likely to resonate with the intended audience
Segmentation helps businesses use their resources more efficiently by focusing on high-potential customer groups rather than wasting efforts on a one-size-fits-all approach.
By understanding these segments, marketing teams (and sales teams) can better craft their messaging so that it is more relevant and likely to resonate with the intended audience. Segmentation helps businesses use their resources more efficiently by focusing on high-potential customer groups rather than wasting efforts on a one-size-fits-all approach.
Benefits of Segmentation
- More accurate and targeted Messaging: Send the right message to the right audience, improving communication effectiveness.
- Efficient Resource Use: Prioritize marketing spend on high-value segments, maximizing ROI.
- Better Customer Understanding: Gain deeper insights into customer needs, enabling more strategic decision-making.
The Role of Personalization
Once segmentation is in place, personalization aims to ensure that each interaction with your customer feels personal and meaningful. Note, the words “aim to ensure” -this is because making something feel personal is tricky to fake. The role of personalization in marketing, is, in essence, making something “feel” personal, when in reality it is not. To make this even harder, we live in an era where customers expect brands to understand their preferences. Today, delivering personalized experiences is no longer a differentiator—it’s a necessity.
How Personalization Elevates Customer Experience
- Relevant Content Delivery: Personalization allows you to serve content that is relevant to each customer’s needs at the right time.
- Increased Loyalty: Customers who feel valued and understood are more likely to stick with your brand over the long term.
- Higher Engagement and Conversion Rates: Personalized interactions drive higher engagement, leading to better conversion rates.
From personalized email campaigns to individualized product recommendations, brands that use personalization effectively are able to foster stronger customer relationships, which directly translates into improved customer satisfaction and business performance.
How Segmentation and Personalization Work Together
Segmentation and personalization are two sides of the same coin. Segmentation lays the groundwork by identifying distinct customer groups, and personalization builds on this by creating unique experiences for each group. Without segmentation, personalization efforts risk being irrelevant, while segmentation without personalization misses the opportunity to engage customers on a deeper level.
For instance, a CRM team might segment their customer base by purchase history, targeting frequent buyers with personalized product recommendations. Or a customer experience team might use behavioral data to segment customers who frequently abandon their shopping carts, sending personalized incentives to encourage them to complete their purchase.
The quality of the data driving your segmentation and personalization is key. Clean, actionable data is critical for making sure you’re reaching the right customers with the right message.
Strategies for Effective Segmentation and Personalization
1. Data Collection and Analysis
Data is the lifeblood of any successful segmentation and personalization strategy. Ensuring that your data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date is essential.
- Use automation tools to regularly clean and validate your data.
- Collect a wide range of customer data, from demographic information to behavioral insights.
2. Creating Customer Segments
Once you’ve gathered enough data, the next step is creating actionable customer segments. Look for patterns in customer behavior as we mentioned earlier, and needs to create well-defined segments.
- Identify key metrics that matter to your business, such as purchase frequency or engagement rate.
- Regularly review and update your segments to keep pace with changing customer behavior.
Approaches to Personalizing Customer Interactions
1. Personalizing Emails
Effective email marketing goes far beyond adding names to subject lines. To step up your email game, there’s a few neat tricks to add some personal touches;
- Segmentation-Based Campaigns: Target your emails at users based on demographics, behaviors, or lifecycle stages (e.g., new customers, cart abandonment).
- Event Triggered Emails: Send personalized emails triggered by user actions (For instance, if a customer recently bought some shoes, email them with an tempting discount some good complimentary socks).
- Dynamic Email Content: Emails are built with dynamic content blocks that pull in personalized information for each user. For instance, one block might show product recommendations based on browsing history, while another displays a location-based offer.
2. Personalizing Website Content
Website personalization customizes the user experience based on real-time data, making content more relevant:
- Geo-Targeting: Show location-specific content, offers, or pricing based on where the user is located.
- Behavioral Personalization: Track user behavior on-site to display relevant products or content based on their browsing history.
- Returning Visitors: Recognize and personalize experiences for repeat visitors, such as showing recently viewed items or personalized offers.
3. Personalizing Product Recommendations
Relevant product recommendations are vital for driving conversions in e-commerce:
- Collaborative Filtering: Suggest products based on the behavior of similar users (e.g., “Customers who bought this also bought…”).
- Content-Based Filtering: Recommend items with similar characteristics to those a user has purchased or viewed.
- Cross-Selling and Upselling: Suggest complementary or higher-end products based on what users have shown interest in.
4. Scaling Personalization with Automation
Automation tools are crucial for scaling personalization efforts across a large audience:
- CRM Systems: Platforms like Salesforce and HubSpot store customer data and automate personalized email and campaign delivery.
- Email Automation Tools: Solutions like Mailchimp and ActiveCampaign allow businesses to create and track personalized email workflows at scale.
- Website Personalization Platforms: Tools like Optimizely and Adobe Target analyze user data in real time to adjust website content dynamically.
- AI-Powered Recommendations: Engines like Amazon Personalize predict and recommend products based on individual user behavior and continuous learning.
- Predictive Analytics: AI tools use predictive analytics to anticipate user behavior (e.g., churn risk) and trigger personalized retention efforts automatically.

Spotify’s Discover Weekly: A Case Study in Effective Personalization
Before we wrap up this article, let’s take a look at what impact a successful personalization strategy can have. You’ve probably heard of Spotify, but did you know they used AI powered personalization to achieve a large part of their success? Spotify’s "Discover Weekly" feature is a prime example of how effective segmentation and personalization can drive business results.
By leveraging user data and machine learning, Spotify created personalized playlists tailored to each listener’s preferences. Users were segmented based on their listening habits and music preferences, enabling Spotify to provide highly individualized recommendations.
The results were nothing less than striking: this single feature increased user engagement substantially, with over 60% of recommended songs being listened to. Additionally, the personalized playlists contributed to higher customer satisfaction and an increase in Spotify’s free-to-premium conversion rates. Within a year of launching "Discover Weekly," over 40 million users were engaging with it, driving both growth and retention. This case highlights how personalized experiences, driven by data and segmentation, can lead to measurable improvements in customer loyalty and conversion.
Measuring Success
To gauge the effectiveness of your segmentation and personalization efforts, track key metrics such as:
- Customer Satisfaction Scores (CSAT): Measure how happy customers are with personalized interactions.
- Engagement Rates: Track email open rates, click-through rates, and on-site engagement.
- Conversion Rates: Monitor how personalized efforts drive conversions.
For example, a company that used Plauti Data Management to clean and analyze their customer data saw a 20% increase in engagement and a 15% boost in conversion rates, thanks to a more targeted and personalized marketing approach.
Conclusion
In today’s customer-centric world, effective segmentation and personalization are no longer optional—they are essential for driving customer satisfaction, engagement, and conversions. By understanding your audience through segmentation and delivering tailored experiences through personalization, you can create a seamless customer journey that builds loyalty and drives business growth.
For marketing teams looking to elevate their segmentation and personalization efforts, Plauti Data Management offers powerful tools to ensure data accuracy and actionable insights. Ready to take your customer experience strategy to the next level?
Talk to an Expert: Schedule a consultation with a Plauti expert to discuss how our data management solutions can help you enhance your segmentation and personalization strategies for better results
Visit www.plauti.com
Talk to an Expert: Schedule a consultation with a Plauti expert to discuss how our data management solutions can help you enhance your segmentation and personalization strategies for better results. Visit www.plauti.com






